Acoustic emission (AE) is the sound waves produced when a material undergoes stress (internal change), as a result of an external force.
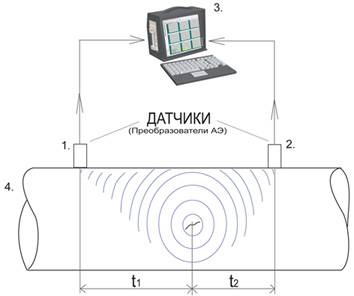
- receiver 1;
- receiver 2;
- computer that collects and handles the information from receivers;
- object to be tested;
t1 – time of the signal going to the first receiver;
t2 – time of the signal going to the second receiver.
The registered time ti of a signal on the i-th receiver (sensor) system defined by the arrival time difference T (T = t2-t1) at spaced receivers. Then known velocity of sound in the material and the known coordinates of receivers program calculates the coordinates of the source (defect). Arrangements of sensors may be different.
Waves propagate from the source to the sensor (s), where they are converted into electrical signals. AE devices detect these signals and display data on the screen as waveforms, locations, digital displays, based on which an operator can evaluate the condition and structure of the material behavior under stress, to detect and locate defects.
The necessity of controlling the high-risk equipment of acoustic emission method:
- long service life;
- every year an increasing failure rate;
- high rate of growth of operational defects in design;
- catastrophic consequences of the destruction of the object.
Using traditional discrete methods of examination becomes ineffective due to the high complexity, the locality of such methods.
Acoustic emission control: detects developing, i.e. the most dangerous defects.
This method is remote; it does not require scanning the surface of the object to search for local defects, but only the correct placement of sensors on the surface of the object to locate the source of the acoustic emission.
Acoustic emission control posibilities
Technical inspection:
- storage tanks
- rail tanks
- isothermal storages of ammonia
- units and systems of refineries and gas processing plants
- compressor stations
- metal structures
Advantages:
- Remote detection and coordinate defects
- Conduct NDT just the whole object in a single cycle of loading
- Quick installation of sensors
- High sensitivity
- Requires local access to the object
- Identifies developing defects
- Requires a relatively small loading
Limits:
- The construction needs to be loaded
- AE activity is strongly dependent on the material and acoustic contact
- When AE-control false signals usually present
- It is difficult to distinguish false signals from useful AE signals
- AE-control gives limited information about the type of defect
| Non-destructive testing | Acoustic emission method |
|---|---|
|
Much complexity of preparatory work and testing itself |
The complexity of the preparatory work and control of tens (hundreds) of times smaller |
|
Impossibility of recognize defects that develop under operating loads |
Detects the most dangerous types of defects that develop under operating loads |
|
For monitoring procedure is required decommissioning the object |
Control can be carried under the conditions of actual use or exposure equivalent test loads |
- For the acoustic emission control insulation coating (if any) is removed only in the place of installation of AE sensors.
- Established NDT methods used for sampling in questionable places determined by the results of acoustic emission monitoring.
- AE-method allows evaluating the technical condition of the construction as a whole as opposed to the sample estimate with other NDT methods.
Control of various types of objects and detected defects:
Rail tanks:
- In the boiler-tank are detected: cracks in the base metal and welds, corrosion and damage throughout the wall (leakage).
- The tank is controlled due to excess pressure pneumatic or hydrotest or by creating a vacuum within the allowable range.
Storage tanks for petroleum products
- Detects defects in inaccessible and the most loaded part of the tank - the bottom and the weld.
- Loading the wall and the bottom of is carried out during filling tank with the product.
Special-purpose vessels (rubberized with non-removable insulating coating or containing expensive catalyst)
- Application of NDT staff due to lack of access is impossible.
- AE-method detects a defect in the metal vessel with minimal disruption of the coating.
- To save the characteristics of non-removable reagent test of vessel is performed using the working environment or an inert gas.
